In 1928, penicillin the world’s first bacteria killing medication was accidentally discovered. This was an outstanding breakthrough, because at that time as well as today, some of the most contagious diseases are caused by bacteria. Since the discovery of penicillin, scientists and doctors have dedicated themselves to perfecting existing antibiotics and finding new ones. Third generation antibiotics on the market today are effective against bacteria, fungi and certain parasites. Every year, doctors write millions of prescriptions for antibiotics, which treat everything from simple skin infections to life-threatening septicemia.
 In 1928, penicillin the world’s first bacteria killing medication was accidentally discovered. This was an outstanding breakthrough, because at that time as well as today, most contagious diseases are caused by bacteria. Since penicillin’s discovery, scientists and doctors have dedicated themselves to perfecting existing antibiotics and finding new ones. Third generation antibiotics on the market today are effective against bacteria, fungi and certain parasites. Every year, doctors write millions of prescriptions for antibiotics, which treat everything from simple skin infections to life-threatening septicemia.
In 1928, penicillin the world’s first bacteria killing medication was accidentally discovered. This was an outstanding breakthrough, because at that time as well as today, most contagious diseases are caused by bacteria. Since penicillin’s discovery, scientists and doctors have dedicated themselves to perfecting existing antibiotics and finding new ones. Third generation antibiotics on the market today are effective against bacteria, fungi and certain parasites. Every year, doctors write millions of prescriptions for antibiotics, which treat everything from simple skin infections to life-threatening septicemia.
Every dose of antibiotics can cause unpleasant side effects and an overdose has the potential to trigger severe side effects. Would you like to know what some of these side effects are?
Side Effects Involving the Digestive Tract
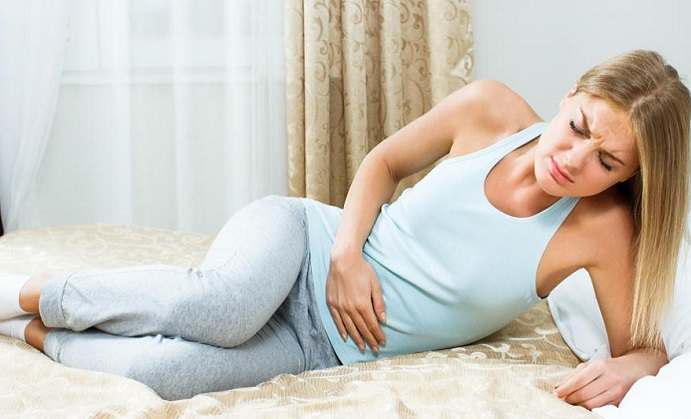
Antibiotics, even when taken in their proper dosage, often affect our stomachs and intestines, and when an overdose is taken, it attacks our digestive tract even more. The mildest symptoms are indigestion accompanied by bloating, and a possible lack of appetite. A particularly strong antibiotic or an overdose can cause severe nausea, vomiting, cramping, and diarrhea as well as abdominal pain.
Side Effects Involving the Respiratory System
 Side effects affecting the respiratory system are not very common, and usually the symptoms are mild to moderate wheezing, coughing and perhaps shortness of breath. These symptoms are similar to a mild allergic reaction, and some doctors treat them with antihistamines.
Side effects affecting the respiratory system are not very common, and usually the symptoms are mild to moderate wheezing, coughing and perhaps shortness of breath. These symptoms are similar to a mild allergic reaction, and some doctors treat them with antihistamines.
In every ten thousand cases, there are between one and five people who will experience a serious allergic reaction to specific antibiotics. These severe allergic reactions quickly escalate into anaphylactic shock. Symptoms of anaphylaxis are a rapid heartbeat, inflammation of the throat which makes breathing difficult, a drop in blood pressure and even the loss of consciousness.
If you or someone you love is having severe shortness of breath after taking an antibiotic, it is critical that you call 911. Calling an emergency number promptly can be the difference between life and death. In the event that someone takes too much antibiotic but is not having difficulty breathing, you should call a poison control center. Be prepared to give them the name of the antibiotic and if possible, the dosage that was taken.
Side Effects Involving the Skin
It is rare that excessive antibiotics trigger a reaction on the skin. When it does happen, the patient may be pale and/or cyanotic and may have a light blue or purple tinge to the lips and nails. They may be especially sensitive to light, and even develop a rash.
Assorted Side Effects
 Antibiotics target harmful bacteria, but they also kill some healthy bacteria, which opens the door for yeast to grow. This overpopulation of yeast can present itself as a vaginal infection in women and as thrush, a yeast infection of the mouth, in both men and women. Any medication we take is distributed throughout our body and then filtered out by the kidneys and liver. Excessive doses of any medicine, and antibiotics in particular, put a heavy load on our whole system and can cause lasting damage to our bone marrow, our kidneys and liver, and other major organs.
Antibiotics target harmful bacteria, but they also kill some healthy bacteria, which opens the door for yeast to grow. This overpopulation of yeast can present itself as a vaginal infection in women and as thrush, a yeast infection of the mouth, in both men and women. Any medication we take is distributed throughout our body and then filtered out by the kidneys and liver. Excessive doses of any medicine, and antibiotics in particular, put a heavy load on our whole system and can cause lasting damage to our bone marrow, our kidneys and liver, and other major organs.
In conclusion, fever, difficulty breathing, pain in the area of the heart, severe vomiting, diarrhea and convulsions indicate a severe reaction to antibiotics and it is important to seek medical attention immediately. If you are experiencing mild reactions to your antibiotic, it is still a good idea to talk with your doctor. He or she may continue the same antibiotic treatment, while helping you find relief from the side effects.